Microfluidics & Soft Matter Group
Indian Institute of Science Education and Research Tirupati
LATEST RESEARCH NEWS
GALLERY OF RESEARCH

Microfluidic droplet generation. Each droplet is 100 micrometer in diameter

Nucleation of Dextran microdroplets at the edge of a drop under evaporation.
The nucleated microdroplets coalesce and advance in a stepwise manner ((Soft Matter, 2024,20, 8260-8266))
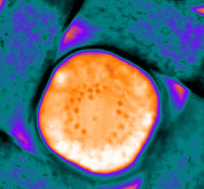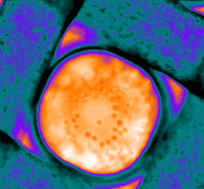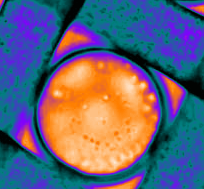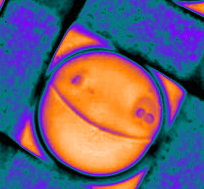
Phase separation of a PEG/dextran microdroplet during evaporation. The nuclei flow inside the droplets and eventually merge to form discrete phases.
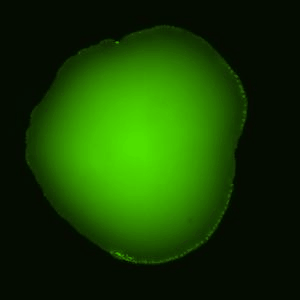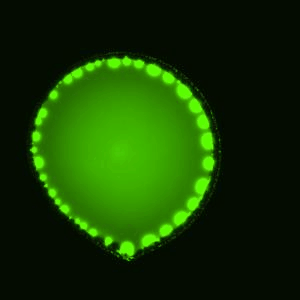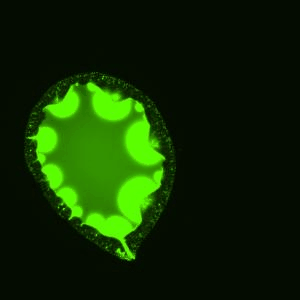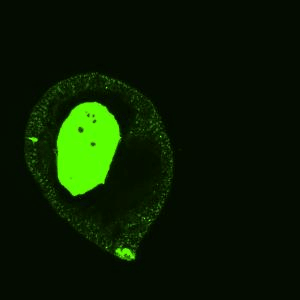
This is a sessile drop of PEG and dextran evaporating on a solid surface. The dextran nucleates upon liquid-liquid phase separation and migrates towards the center of the drop. Our study explains how these dynamics evolves over time (Soft Matter, 2024,20, 8260-8266)

Bacteria (Mycobacterium smegmatis) replicate and forms a colony. We study how salt affects their growth and response to antibiotics.

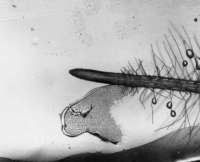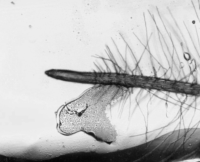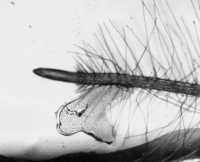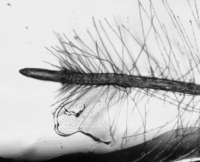
Arabidopsis thaliana grown on a microfluidic chip. Timelapse image of the root growth.

Microfluidic emulsion droplets evaporate in a gradient manner (Physics of Fluids 34 (2022)).
Quincke rotation of snowman shaped particles JCIS Open, 15, 2024
OUR LAB
.jpg)







